Communism Vs Marxism: A Deep Dive Into The Core Differences
When it comes to political ideologies, communism and Marxism often get thrown into the same basket. But hold up, there's more to the story than meets the eye. If you're scratching your head wondering what exactly separates these two heavyweights of political thought, you're in the right place. In this article, we're diving headfirst into the world of communism vs Marxism, breaking down the differences and similarities in a way that even your grandma could understand. So buckle up, because we're about to take a wild ride through the history books and political theory land.
Now, before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let's set the stage. Both communism and Marxism are rooted in the idea of creating a fairer society, but they approach this goal from slightly different angles. Think of them as cousins at a family reunion – they share some DNA, but their personalities couldn't be more different. As we explore this topic, we'll uncover the nuances that make each ideology unique and why they continue to spark heated debates around the globe.
One thing's for sure: understanding the differences between communism vs Marxism isn't just about impressing your friends at dinner parties. It's about grasping the forces that have shaped our world and continue to influence political movements today. So, whether you're a history buff, a political science student, or just someone curious about the world, this article's got you covered.
- Vegamovies Bollywood Hollywood Mehr Dein Filmparadies
- Vegamovies Dein Ultimativer Ort Fr Filmstreaming Entdecke Es
What is Communism? The Basics You Need to Know
Alright, let's start with the big C – communism. At its core, communism is a political and economic ideology that aims to create a classless society where all property and resources are owned collectively by the community. In theory, this means no rich, no poor, just everyone living harmoniously under the same roof. Sounds utopian, right? But like most things in life, the reality is a little more complicated.
Communism gained traction in the 19th century as a response to the inequalities of capitalism. Think about it – while a small group of people were raking in the dough, the majority were struggling to make ends meet. Enter Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, who argued that the only way to fix this imbalance was to abolish private property and establish a system where everyone contributed according to their ability and received according to their needs.
But here's the kicker – communism isn't just a theory. It's been put into practice in various countries, with mixed results. Some argue that it's the key to a fairer world, while others claim it's a recipe for disaster. As we'll explore later, the implementation of communism has led to some pretty intense debates about its effectiveness and feasibility.
- Filmhighlights James Bond Vega Mehr Alles Was Du Wissen Musst
- Filme Online Schauen Legal Sicher Alternativen Zu Hdhub4u
Key Principles of Communism
- Elimination of private property
- Collective ownership of resources
- Classless society
- Equality for all citizens
These principles may sound simple, but putting them into action is a whole different ball game. Imagine trying to convince a billionaire to give up their mansion for the greater good. Not exactly an easy sell, right?
Marxism: The Brainchild of Karl Marx
Now let's shift gears and talk about Marxism. This ideology was born in the mind of one Karl Marx, a philosopher and economist who lived during the 19th century. Marxism is essentially the blueprint for communism, outlining the theory behind why a classless society is necessary and how it can be achieved.
Marx believed that history was driven by class struggles – the conflict between those who owned the means of production (the bourgeoisie) and those who worked for them (the proletariat). In his view, capitalism was inherently flawed because it created a system where the rich got richer and the poor got poorer. The solution? A revolution that would overthrow the existing order and establish a socialist state, which would eventually evolve into a communist society.
But here's the twist – Marxism isn't just about economics. It's also about culture, politics, and pretty much every aspect of society. Marx believed that the way we think, act, and interact is shaped by the economic system we live in. So, if you want to change society, you have to change the economic foundation first.
Key Principles of Marxism
- Class struggle as the driving force of history
- Revolutionary change to overthrow capitalism
- Transition from socialism to communism
- Analysis of economic and social structures
While Marxism provides a detailed roadmap for achieving communism, it's important to note that not all Marxists are communists, and not all communists are Marxists. Confused yet? Don't worry, we'll untangle this web of ideologies as we go along.
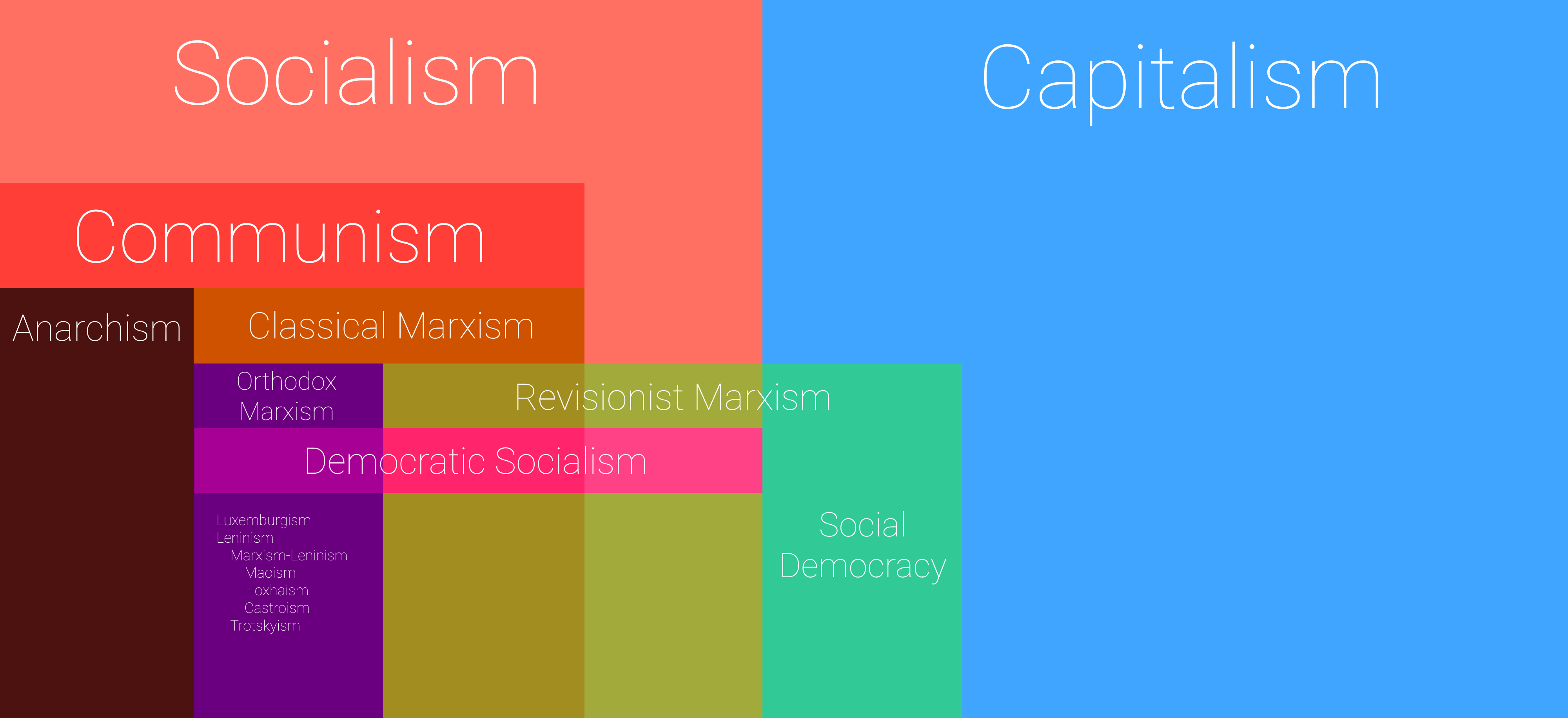
Communism vs Marxism: The Key Differences
Now that we've covered the basics of both communism and Marxism, let's dive into the differences. While they share some similarities, there are some key distinctions that set them apart. Think of it like this – Marxism is the theory, while communism is the practice. One is the blueprint, the other is the building.
One of the main differences lies in their scope. Marxism is a comprehensive theory that covers everything from economics to culture, while communism is more focused on the practical implementation of a classless society. Marxism provides the "why" and the "how," while communism deals with the "what."
Another important distinction is the role of the state. In Marxism, the state is seen as a tool for achieving socialism, which will eventually lead to communism. However, in communism, the state is seen as unnecessary once the transition to a classless society is complete. This difference in perspective has led to some heated debates among political theorists.
Table: Key Differences Between Communism and Marxism
| Aspect | Communism | Marxism |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Practical implementation | Theoretical framework |
| State Role | Abolition of the state | Use of the state to achieve socialism |
| Scope | Narrower focus on economic and social systems | Broader focus on culture, politics, and society |
This table should give you a clearer picture of how these two ideologies differ, even though they share some common goals.
Historical Context: How Communism and Marxism Shaped the World
Understanding the historical context of communism vs Marxism is crucial to grasping their impact on the world. Both ideologies emerged during a time of rapid industrialization and social change, where the gap between the rich and poor was widening by the day. It was in this fertile ground that Marx and Engels planted the seeds of their revolutionary ideas.
Throughout the 20th century, communism and Marxism influenced countless political movements and revolutions. From the Russian Revolution to the Chinese Civil War, these ideologies have left an indelible mark on global history. Some countries embraced communism wholeheartedly, while others rejected it outright. The Cold War, in particular, saw a fierce battle between communist and capitalist ideologies, shaping the geopolitical landscape for decades.
But history isn't just about the big events. It's also about the everyday people who lived through these changes. Imagine being a worker in the Soviet Union during the height of communism, or a peasant in China during the Cultural Revolution. These experiences offer valuable insights into the practical implications of these ideologies.
Impact on Modern Politics
Even today, the legacy of communism and Marxism continues to influence modern politics. From socialist movements in Europe to progressive policies in the United States, the ideas put forth by Marx and Engels are still relevant. However, the way these ideas are interpreted and applied varies greatly depending on the context.
Communism vs Marxism in Practice: Case Studies
Let's take a closer look at how communism and Marxism have been put into practice in different parts of the world. By examining specific case studies, we can gain a deeper understanding of their strengths and weaknesses.
In the Soviet Union, communism was implemented on a massive scale, with mixed results. While it achieved some successes in terms of education and healthcare, it also faced significant challenges, including economic inefficiencies and political repression. Similarly, in China, the implementation of communism under Mao Zedong led to both achievements and setbacks, shaping the country's development in profound ways.
On the other hand, Marxism has influenced various socialist movements around the globe, from Latin America to Africa. These movements have sought to address issues such as inequality, poverty, and social injustice, often with varying degrees of success.
Lessons Learned
What can we learn from these case studies? For one, implementing communism or Marxism is a complex and challenging process that requires careful consideration of local conditions and contexts. There's no one-size-fits-all solution, and what works in one country may not work in another.
Common Misconceptions: Setting the Record Straight
There are a lot of misconceptions floating around about communism vs Marxism, and it's time to set the record straight. For starters, not all communists are Marxists, and not all Marxists are communists. While the two ideologies are closely related, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Another common misconception is that communism is inherently oppressive or undemocratic. While some communist regimes have been guilty of human rights abuses, it's important to remember that the ideology itself doesn't necessarily dictate such outcomes. Similarly, Marxism is often misunderstood as being anti-capitalist to the extreme, when in reality it offers a nuanced critique of capitalism's flaws.
Clarifying the Confusion
By addressing these misconceptions, we can foster a more informed and nuanced understanding of communism vs Marxism. It's important to approach these ideologies with an open mind and a willingness to learn from history.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Communism vs Marxism Matters
As we wrap up this deep dive into communism vs Marxism, it's clear that these ideologies continue to shape our world in significant ways. Whether you're a die-hard Marxist or a staunch anti-communist, understanding the differences and similarities between these two schools of thought is essential for making sense of the complex political landscape we live in today.
We encourage you to join the conversation by leaving a comment below or sharing this article with your friends. The more we talk about these issues, the better equipped we'll be to tackle the challenges of tomorrow. So, what are you waiting for? Let's get the discussion started!
Table of Contents
- What is Communism? The Basics You Need to Know
- Marxism: The Brainchild of Karl Marx
- Communism vs Marxism: The Key Differences
- Historical Context: How Communism and Marxism Shaped the World
- Communism vs Marxism in Practice: Case Studies
- Common Misconceptions: Setting the Record Straight
- Conclusion: Why Understanding Communism vs Marxism Matters


Detail Author:
- Name : Annie Sauer
- Username : rosario.barton
- Email : ioconner@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1972-03-08
- Address : 89581 Boehm Freeway North Justusfurt, CA 98302
- Phone : +1 (908) 508-9570
- Company : McCullough and Sons
- Job : Drafter
- Bio : Omnis quis reprehenderit ipsum numquam. A porro et quo similique nihil eum et similique. Quibusdam qui deleniti eum eos est. Quia nulla dolore repellat architecto quis.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/hermannn
- username : hermannn
- bio : Autem ullam ut minima ratione laborum. Ut laboriosam eius optio.
- followers : 4854
- following : 2217
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/hermannn
- username : hermannn
- bio : Iste corrupti quia officiis maxime.
- followers : 455
- following : 927
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@norberto.hermann
- username : norberto.hermann
- bio : Est voluptatem cum ut repellat.
- followers : 6606
- following : 466